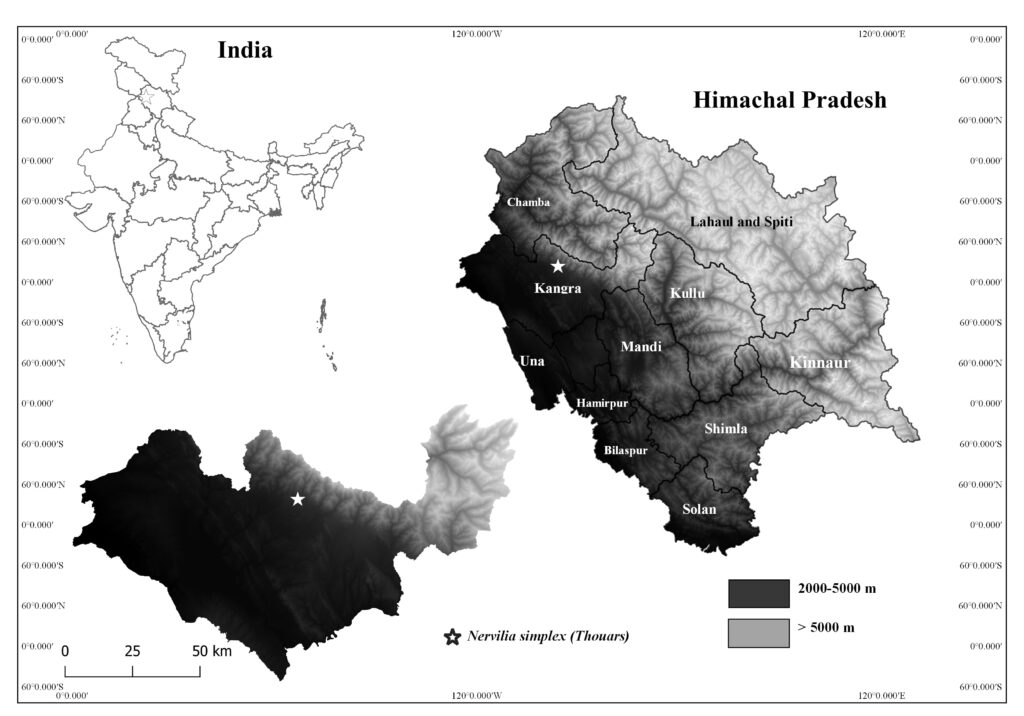
Scutellaria is a large, subcosmopolitan genus of the Labiatae with 425 currently recognised species. However, the actual number is closer to 360 due to a large number which doubtfully merit specific status being recognised in the USSR and China (Paton 1990). The name Scutellaria, from the Latin word scutella meaning a dish, referring to the dish-like scutellum of some European species, was first used by Cortuso (1591) as an alternative name for Lamium peregrinum. Morison (1669) was first to suggest that Scutellaria should be given generic status. The English common name Skullcap and the French la Toque refer to the name Cassida, meaning a metal helmet, given by Colonna (1616). Bentham (1834) placed Scutellaria along with Prunella L. and Cleonia L. in the tribe Scutellarineae on account of the superficial calyx resemblance. Visiani (1847) removed Cleonia and Prunella which seems sensible. However Bentham (1848 and 1876) kept these genera together and merged them into the large tribe Stachydeae. This group does not seem natural and does not reflect the apparently isolated position of Scutellaria within the Labiatae. Caruel (1886), emphasising the character of the curved or bent embryo, placed Scutellaria, Perilomia and Salazaria in a new family-the Scutellariaceae, Scutellaria and its allies differ from the rest of the Lamioideae in lacking endosperm. According to a database of POWO, The native range of Scutellaria is Cosmopolitan and portrayed by ten species reported in India: Scutellaria barbata D.Don, Scutellaria discolor Wall. ex Benth., Scutellaria galericulata L., Scutellaria grossa Wall., Scutellaria heydei Hook.f., Scutellaria linearis Benth., Scutellaria prostrata Jacquem. ex Benth., Scutellaria repens Buch.-Ham. ex D.Don, Scutellaria scandens D.Don, Scutellaria violacea B.Heyne ex Benth.
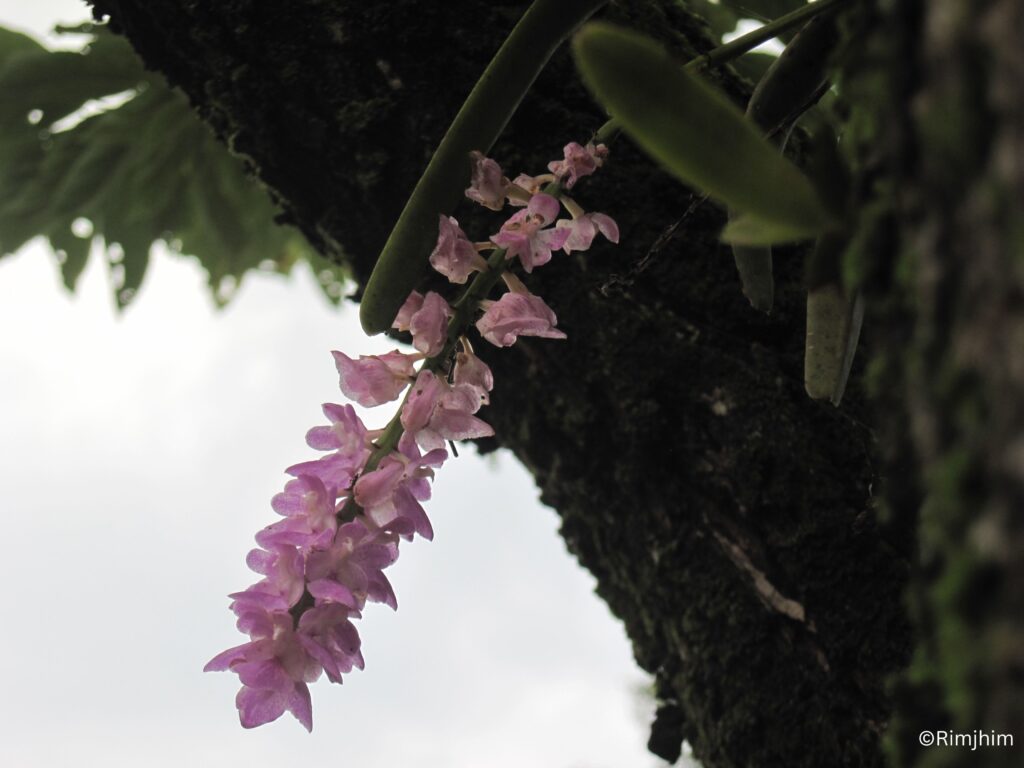
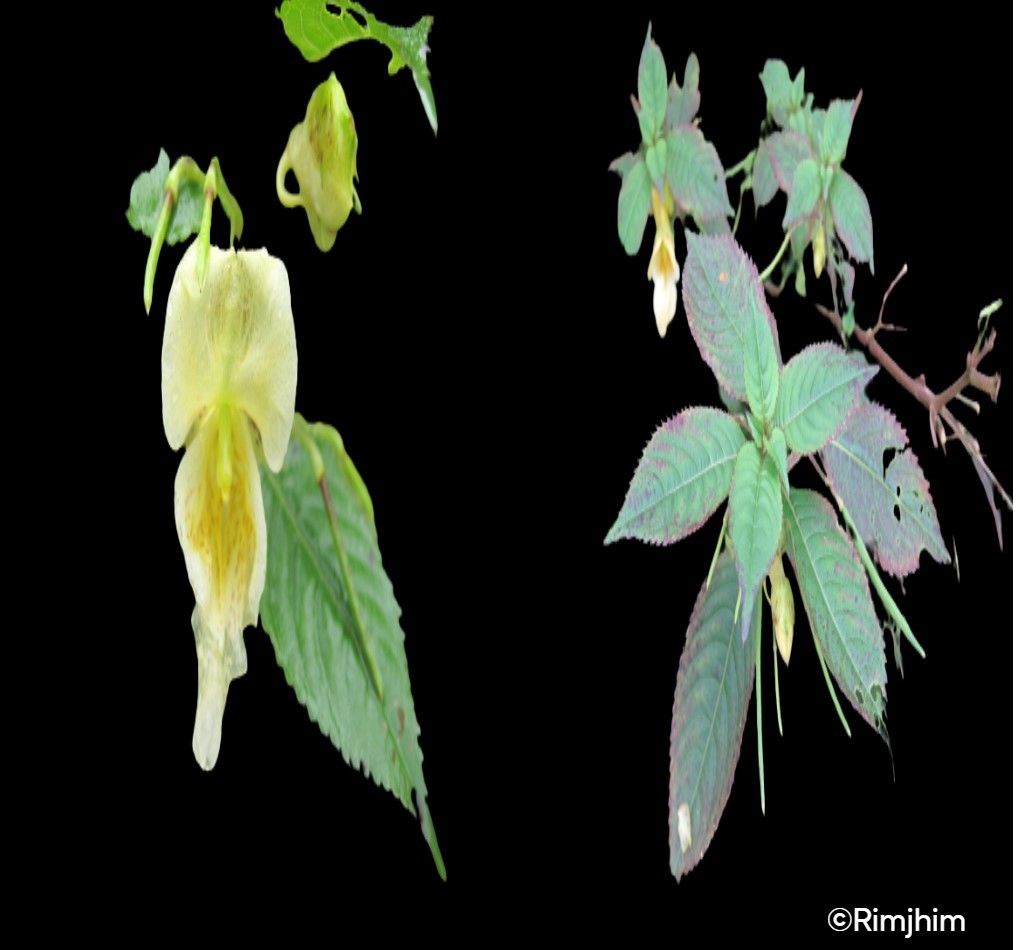
Scutellaria discolor Wall. ex Benth.
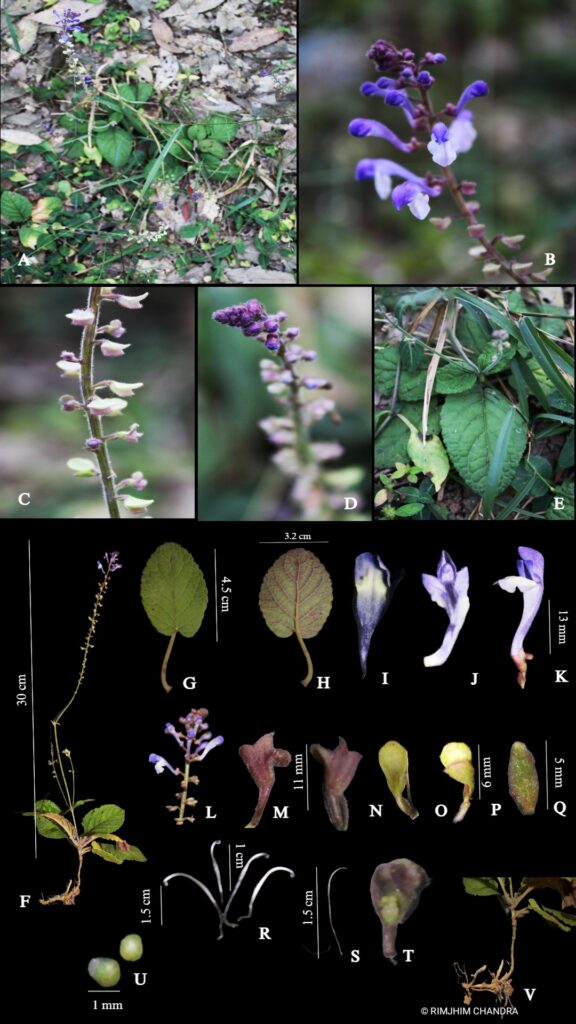
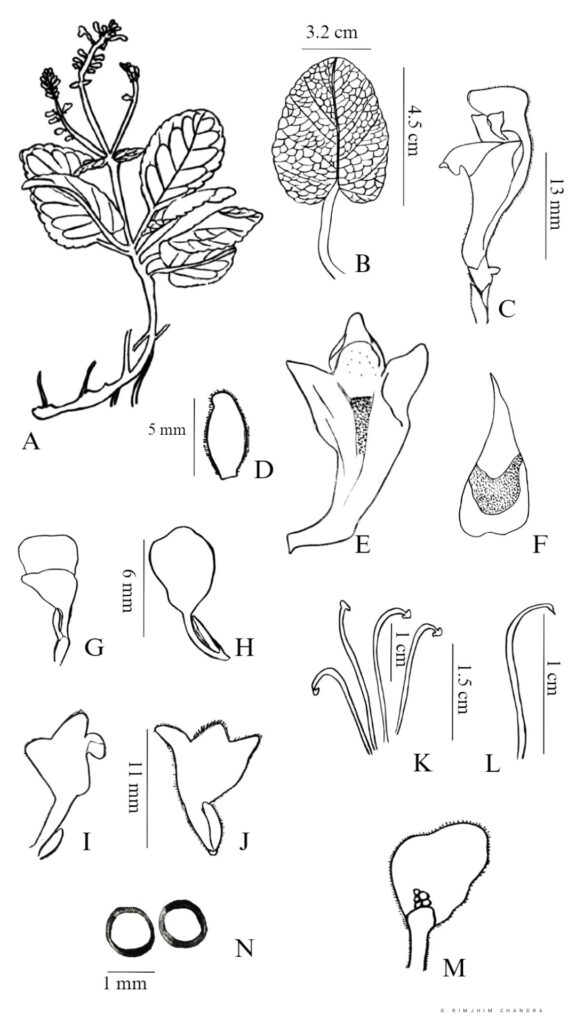

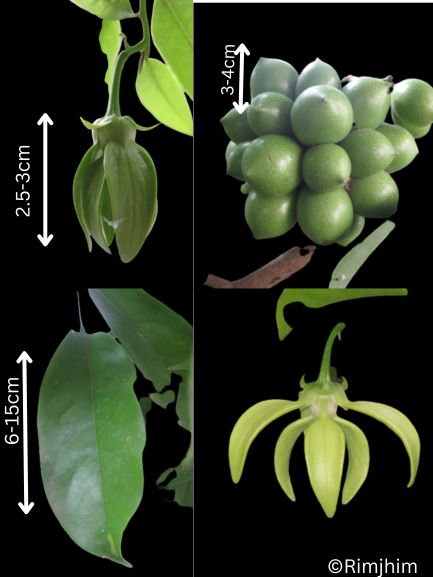
Q. Floral leaf; R. Stamen; S. Carpel; T. U. Fruit, Nutlet; V. Rhizome.
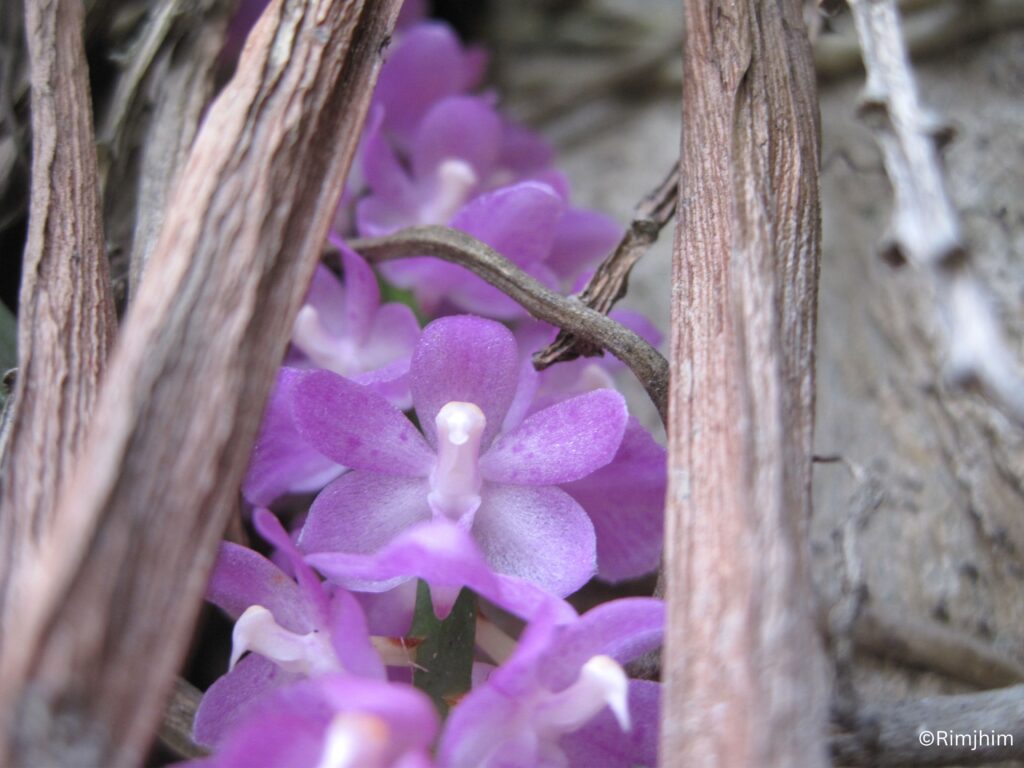
Scutellaria discolor Wall. ex Benth.
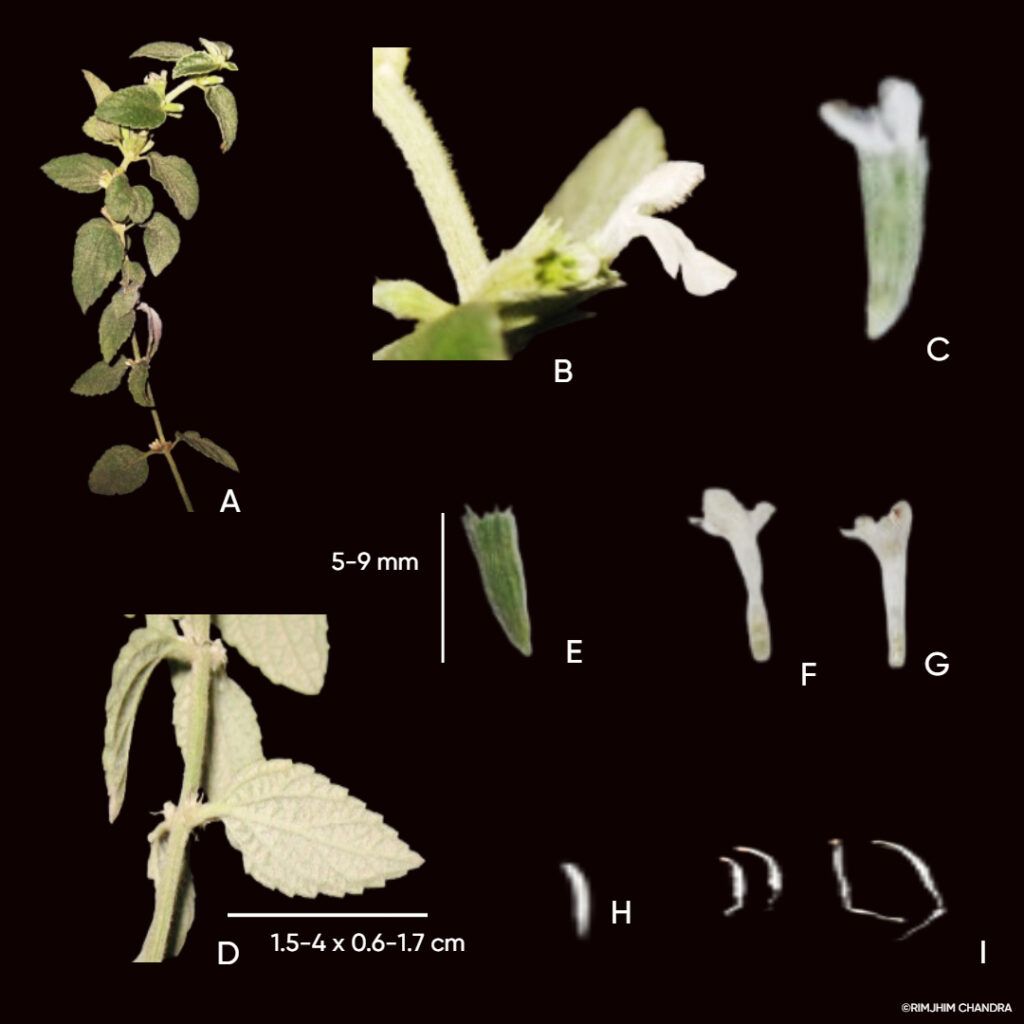
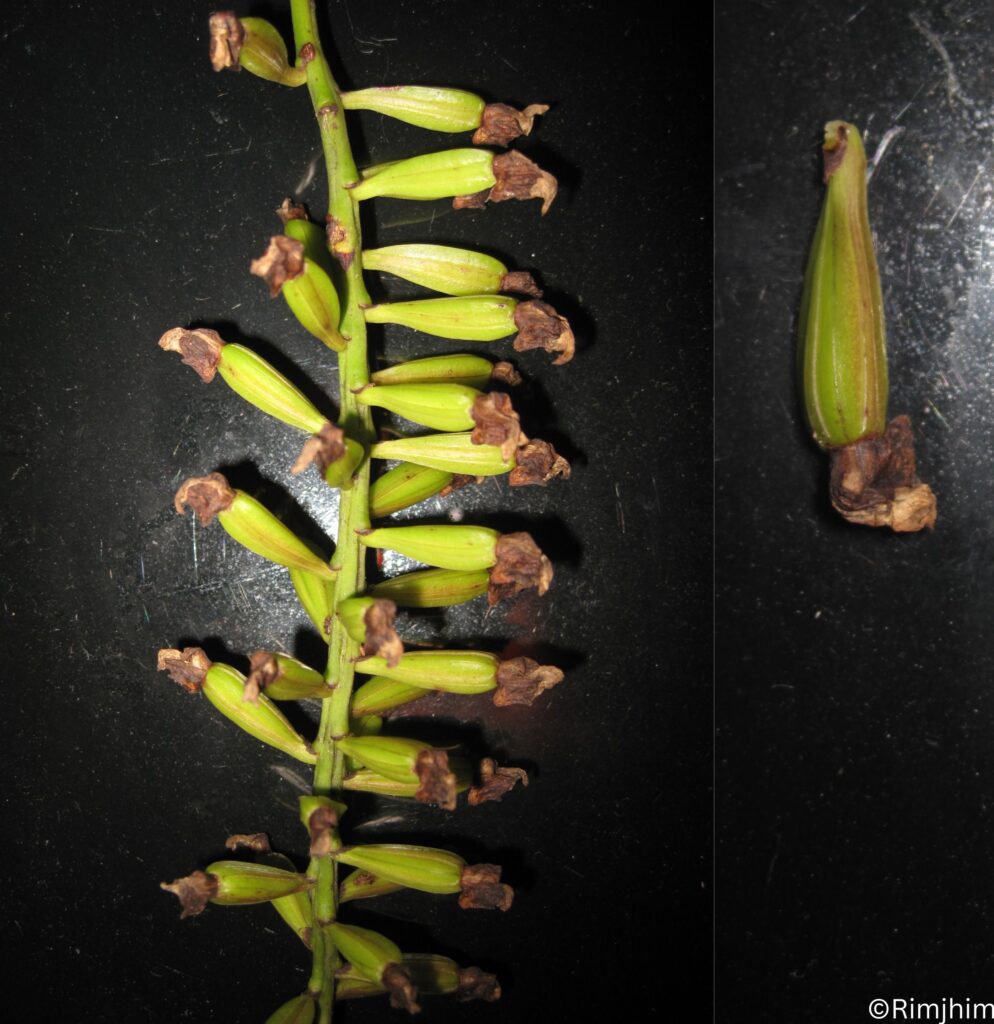
Herbs perennial, rhizomatous. Stems ascending to erect, 5.5-38 cm tall, densely puberulent, reddish, unbranched, apically leafless. Stem leaves in 2-4(-7) pairs; petiole 0.5-2.2(-4.8) cm; leaf blade elliptic-ovate to broadly elliptic, 1.5-7.4 × 1-4.8 cm, papery, pubescent or hirsute especially on veins, adaxially densely puberulent to hirsute, abaxially green or purplish, base cordate to shallowly cordate, margin undulate-crenate, apex rounded to obtuse. Racemes secund, 5-24 cm; peduncle 2.5-4 cm, densely puberulent; floral leaves sessile to short petiolate, ovate to elliptic, 0.7-2.5 × 0.5-1.5 cm, base rounded-truncate, apex obtuse; bracts ovate, 1.5-3 × ca. 1 mm, pubescent, margin entire. Flowers alternate or opposite. Pedicel purplish, 2.5-3 mm, densely pubescent. Calyx ca. 2 mm, pubescent outside, glandular pubescent; scutellum spreading, semicircular, 0.5-0.8 mm, reflexed, almost as long as calyx in fruit. Corolla purple, glandular pubescent outside, 0.9-1.2 cm; tube 7-10 mm, base bent, gradually dilated to 3 mm wide at throat; limb ca. 3 mm, puberulent or pubescent inside; middle lobe of lower lip ovate-orbicular; lateral lobes ovate to oblong-ovate. Nutlets brown, ovoid-ellipsoid, ca. 1 mm in diam., with acuminate tubercles tipped by a whorl of hooks.
Flowering: Jun-November
Fruiting: July- December.